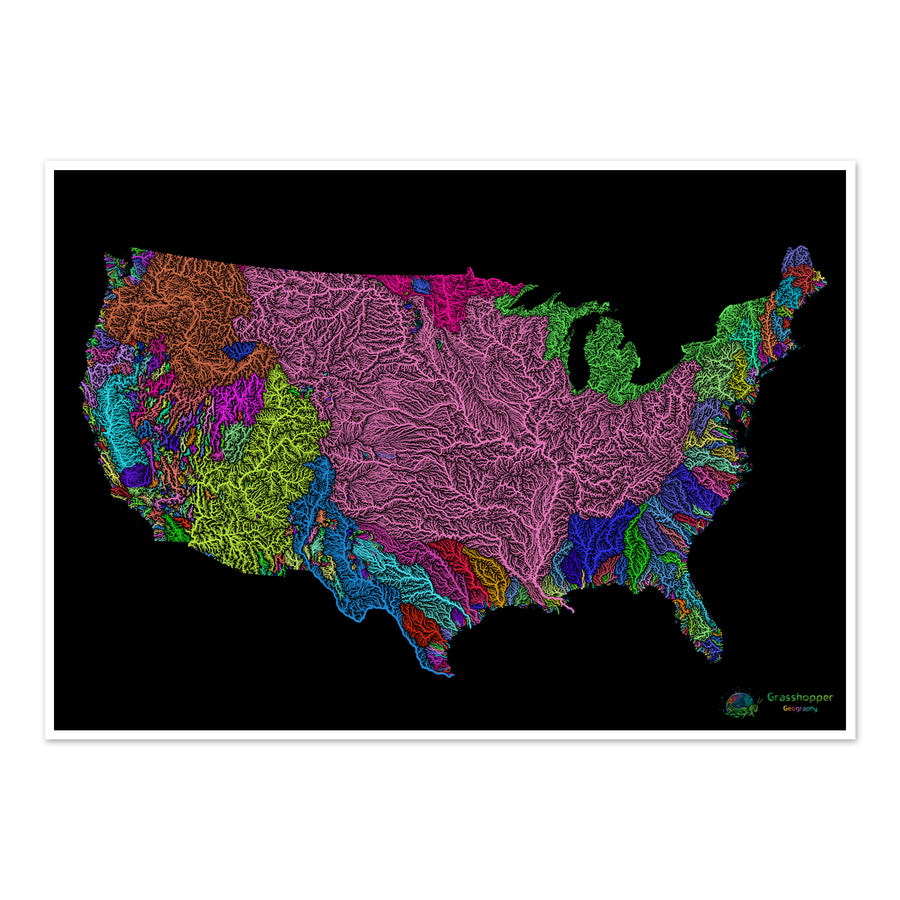
Glossary
You always paid attention in Geography classes, but still not sure what a watershed is?
Thanks to different dialects and language use, these definitions can be really tricky. Here you can find help on talking about your maps in a more accurate, scientific way.
So what is a watershed?
A watershed, by one definition, is any area of land where precipitation collects and drains into a common outlet, such as a river, lake, ocean, or any other body of water. It includes all of the surface water from precipitation runoff and snowmelt, as well as all of the groundwater beneath the Earth's surface.
However, a watershed can also mean the elevated terrain that separates neighbouring drainage basins.
Confused? No wonder. English linguistics never fails to amaze me either.
River basin vs watershed vs drainage divide
In North America a watershed is also known as a river basin, so the two can be used interchangeably. Catchment area, drainage area, drainage basin or water basin can also mean the same funnel-like area that is usually surrounded by ridges, hills or mountains. This connected height of land is also known as a drainage divide, as they divide the different water drainage areas. Basically, watersheds (or river basins) are separated by the drainage divide.
Outside North America though, watershed means the drainage divide itself: all the mountains, hills and ridges that surround the river basin. Synonyms would be water divide, divide, ridgeline or water parting. In this case, river basins are separated by a watershed.
Hope this saved you some time on searching for the right definition.
Below you can find a glossary of other useful geography terms that might come in handy when talking about our maps.
affluent
Also called a tributary. A stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem or a lake, rather than directly into a sea or ocean. Contrast distributary.
confluence
The place at which two or more rivers or other watercourses flow together to form one larger river or watercourse.
delta
A landform at the mouth of a river where the main stem splits up into several distributaries. It is formed from the deposition of the sediment carried by the river as the flow leaves the mouth of the river. Compare estuary.
distributary
A stream or river that branches off and flows away from a main channel. Distributaries are common near river deltas. Contrast tributary.
elevation map
Also called a relief map. A type
of topographic map that uses contour lines or colours to represent the three-dimensional features of a landscape on a two-dimensional surface.
estuary
The broad lower course of a river where it enters the ocean and is affected by the tides. Compare delta.
relief map
Also called an elevation map. A type of topographic map that mainly uses colours to represent the three-dimensional features of a landscape on a two-dimensional surface.
tributary
Also called an affluent. A stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem or a lake, rather than directly into a sea or ocean. Contrast distributary.
(Main source: previous studies and Wikipedia)
Why are watersheds important?
What are watersheds? How to find them? Why are they important? Watch permaculture instructor Andrew Millison's highly informative video if you want to know more.
Another good knowledge booster video on watersheds can be found here, made by Time for Geography.